
Suspendisse interdum consectetur libero id. Fermentum leo vel orci porta non. Euismod viverra nibh cras pulvinar suspen.
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure performed to replace a damaged or deteriorated knee joint with an artificial one, called a prosthesis. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who have severe knee pain, limited mobility, and decreased quality of life due to conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic injury to the knee.
Here is a brief overview of the knee replacement procedure:
Preparation: Before the surgery, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests (like X-rays and MRI). The surgeon will discuss the procedure, risks, and benefits, and provide instructions on pre-surgery preparations.
Anesthesia: Knee replacement surgery is typically performed under either general anesthesia (where you are unconscious) or regional anesthesia (epidural or spinal anesthesia, which numbs the lower half of your body).
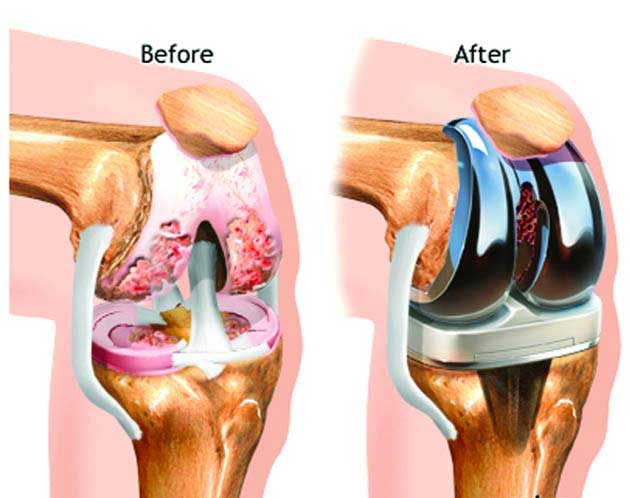
Incision: The surgeon makes an incision over the knee joint, exposing the damaged bone and cartilage.
Reshaping the Bones: The damaged surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia) are removed, and the bones are reshaped to fit the prosthetic components.
Implantation: The artificial knee joint, which consists of metal and plastic components, is securely attached to the prepared bone surfaces. The components may be cemented in place.
Balancing and Alignment: The surgeon ensures that the prosthetic components are properly aligned and balanced, allowing for optimal joint function.
Closure: The incision is closed with stitches or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Recovery: After surgery, the patient is monitored in a recovery area and then moved to a hospital room. Physical therapy and pain management are crucial aspects of the recovery process.
Postoperative Care: Patients typically stay in the hospital for a few days, depending on their progress. Physical therapy is initiated to help regain strength and mobility in the knee.
Return to Normal Activities: The timeline for returning to normal activities varies from person to person but may take several weeks to months. Most patients experience significant improvement in pain and function after knee replacement.
It's essential to follow the surgeon's instructions regarding postoperative care, rehabilitation exercises, and activity restrictions to ensure a successful recovery. Knee replacement surgery has a high success rate in relieving pain and improving knee function, allowing many individuals to resume an active lifestyle with reduced pain and increased mobility. However, it also carries risks, including infection, blood clots, and implant wear over time, so it's crucial to have a thorough discussion with your healthcare provider to determine if knee replacement is the right option for you.